Note:
This topic has been translated from a Chinese forum by GPT and might contain errors.
Original topic: ADMIN CANCEL DDL与kill session_id区别
Version V6.5.6
Dear experts, what is the difference in the execution process between ADMIN CANCEL DDL and kill session_id?
- Target Object: Setting
tidb_mem_oom_action to CANCEL controls the memory usage of a single SQL query, while KILL process_id terminates the entire process or session.
- Execution Timing:
CANCEL is automatically triggered when the memory usage of an SQL query exceeds the set threshold, whereas KILL is manually executed by the user as needed.
- Impact Scope:
CANCEL only affects the single SQL query that meets the trigger condition, while KILL may affect all queries and operations being executed by that process.
- Feedback Mechanism:
CANCEL returns detailed error information to the client, whereas the feedback from KILL may be relatively simple, merely indicating that the process has been terminated.
In summary, there are clear differences in the execution process and purpose of setting tidb_mem_oom_action to CANCEL and using KILL process_id in TiDB. The choice of which method to use depends on specific needs and scenarios.
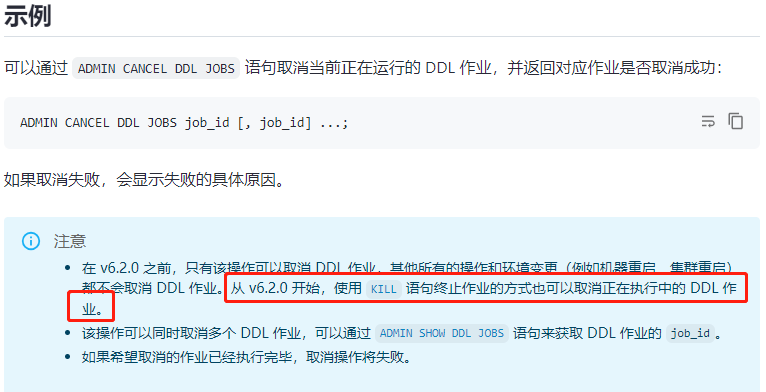
ADMIN CANCEL DDL is specifically used for DDL operations, while KILL SESSION_ID can terminate any type of session.
The difference was greater before v6.2.0.
Are the cancellation execution processes for DDL the same for the two statements after V6.2.0?
 I couldn’t find similar information, so I can only wait for the source code experts to answer.
I couldn’t find similar information, so I can only wait for the source code experts to answer.
After version 6.2.0, both can handle DDL. It is speculated that the difference might be that “force abort” is more aggressive, while “cancel” should be more gentle. This is purely personal speculation.
I have already studied the answers from the experts. By the way, I have a question: does using kill process id to terminate the execution of an SQL statement feel too coarse-grained? Is there no way to directly terminate the currently executing SQL statement and return an abort abnormally?
This should not be the case, both Oracle and MySQL kill sessions.
It doesn’t seem to be supported.
Pressing Ctrl+C can also stop it, but it’s relatively slow.
ADMIN CANCEL DDL: Used to cancel an ongoing DDL task.
kill session_id: Used to terminate the entire database session, including any type of operations that may be in progress, such as DDL, DML, etc.
Ah? No way, I saw in the official documentation that ctrl+c only terminates the connection, the SQL statement is still running.
The process might be similar, just with different objects of operation.
One is DDL Job, and the other is Session.
My understanding is the same. Ctrl+C can only terminate the connection, but it cannot terminate the statements that have already been sent to the database and are still being executed in the database.