Note:
This topic has been translated from a Chinese forum by GPT and might contain errors.
Original topic: GC正常但还是显示“含已删除或覆盖但未 GC 的版本”数太多
[TiDB Usage Environment] Production
[TiDB Version] 5.2.2
[Encountered Problem] Simple queries are very slow
[Reproduction Path]
[Problem Phenomenon and Impact]
[Attachments]
Please provide the version information of each component, such as cdc/tikv, which can be obtained by executing cdc version/tikv-server --version.
This kind of problem can only be avoided by preventing full table scans. I shared this before 
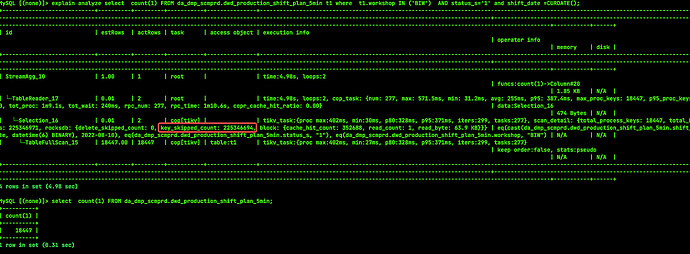
Selecting count(1) from table t is very fast and only takes 0.x seconds, while the query with conditions shown in the picture above takes around 5 seconds.
Could you please share the article again? I couldn’t find it.
“select count(1) from t” directly uses the primary key index and will not perform a full table scan.
Offline event in Wuhan,
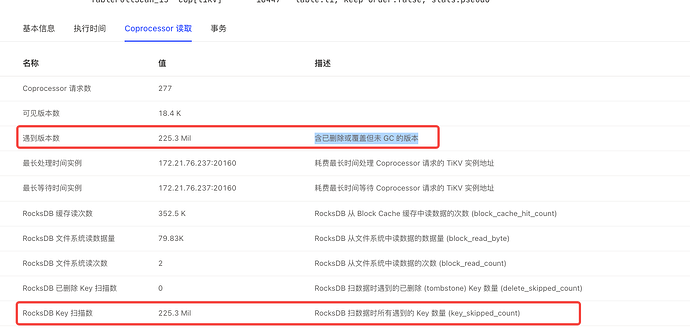
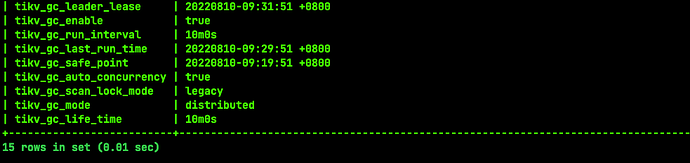
I saw the article by the expert, which mentioned avoiding full table scans and GC. Currently, my entire table has 18,000 rows of data, and GC is functioning normally. I just don’t understand why there are still so many expired keys. Moreover, when I execute the same statement again, the execution plan is the same, but when it executes quickly, there is no key_skipped_count.
It is possible that this bug has not met the GC conditions and requires manual compaction.
The pitfalls have been pointed out to you, make sure to avoid them in time 
I see that the regions of this table are distributed across all TiKV and TiFlash nodes… Do I need to perform this tikvctl operation on all 10+ machines?
Yes, I see it. Thank you! Do I have to use tikv-ctl to execute commands on each TiKV node? Is there a quicker way to handle this? This table is frequently truncated.
You can also operate in a cluster manner.
Manually compact the data of the entire TiKV cluster
The compact-cluster command can manually compact the entire TiKV cluster. The meaning and usage of the parameters of this command are the same as those of the compact command.
What is the impact of compacting the entire cluster on the business, and what should be noted?
I don’t know how big the risk is and how long the execution time will be; the cluster is very large.
You can reduce the concurrency, and it’s best to test with UAT resources, which would be the most reliable.
May I ask if the issue has been resolved? Was it resolved through manual compaction? Please share, thanks.
Temporarily bypass the bug and wait for a fix. 
The cluster is too large and uncontrollable, so I didn’t operate it.
This topic was automatically closed 1 minute after the last reply. No new replies are allowed.